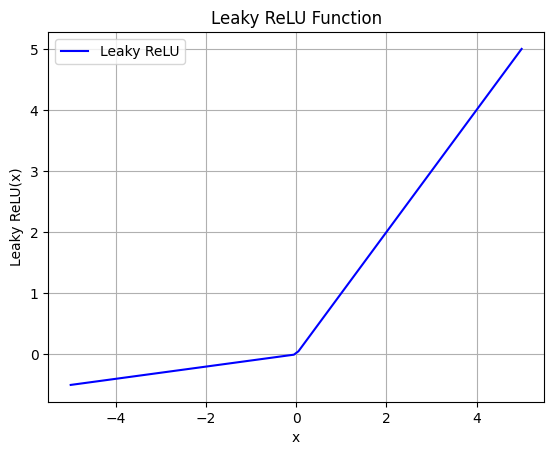
The Leaky Rectified Linear Unit (Leaky ReLU) is a variant of the ReLU activation function that allows a small, positive slope for negative input values, rather than setting them to zero. It is defined as:
Where:
- is the input to the function.
- is a small positive slope (typically a small constant, e.g., 0.01).
Explanation
Leaky ReLU is used as an alternative to the traditional ReLU activation function for several reasons:
-
Prevent Dying ReLU Problem: In traditional ReLU, neurons may become “dead” during training, where they consistently output zero for all inputs. Leaky ReLU addresses this issue by allowing a small, non-zero gradient for negative input values, which prevents neurons from becoming inactive.
-
Avoid Zero Gradient: ReLU sets all negative values to zero, resulting in zero gradients during the backward pass in training. Leaky ReLU ensures that there is always a non-zero gradient, which helps in learning even when the input is negative.
-
Reduced Sensitivity to Hyperparameters: Leaky ReLU introduces a small slope parameter (typically a small constant like 0.01). This parameter is less sensitive to changes compared to the threshold parameter in ReLU, making Leaky ReLU more robust to variations in hyperparameters.
-
Sparse Activation: Leaky ReLU allows for sparse activation by allowing negative values to propagate through the network, which can be beneficial for certain types of data and tasks.
Overall, Leaky ReLU is preferred over traditional ReLU in scenarios where the dying ReLU problem is observed, or where a non-zero gradient for negative inputs is desirable for improved training stability and convergence.
Live example
TODO impelement theme change
Python implementation
Here’s how you can implement the Leaky ReLU function in Python:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define the Leaky ReLU function
def leaky_relu(x, alpha=0.1):
return np.maximum(alpha * x, x)
# Generate x values
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100)
# Compute the corresponding y values using Leaky ReLU
y = leaky_relu(x)
# Plot the Leaky ReLU function
plt.plot(x, y, label='Leaky ReLU', color='blue')
# Add labels and title
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('Leaky ReLU(x)')
plt.title('Leaky ReLU Function')
# Add a grid
plt.grid(True)
# Add a legend
plt.legend()
# Show the plot
plt.show()Output: