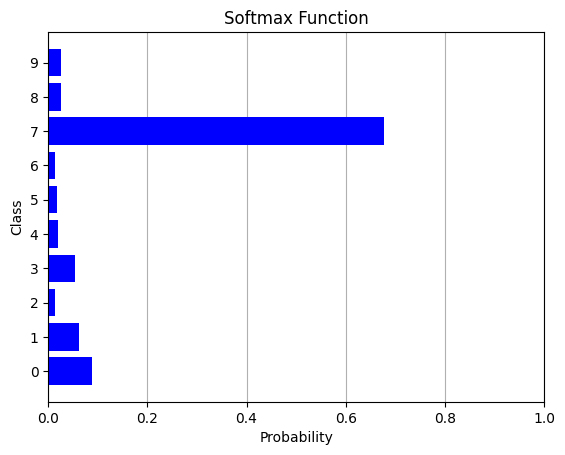
The softmax function is a mathematical function that converts a vector of real numbers to a probability distribution. It is often used as the activation function in the output layer of a neural network for multi-class classification problems.
Mathematically, the softmax function is defined as:
Where:
- is the element of the input vector .
- is the total number of elements in the vector.
- is Euler’s number, approximately equal to 2.71828.
The softmax function exponentiates each element of the input vector and then normalizes the results to ensure that they sum up to 1, thus producing a valid probability distribution.
In the context of neural networks, the softmax function is typically applied to the output layer to convert the raw output scores (logits) into probabilities for each class.
Here’s a Python example of the softmax function:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def softmax(z):
exp_z = np.e ** z
return exp_z / np.sum(exp_z)
num_classes = 10
# Generate very small values
z = (np.random.rand(num_classes)-0.5)*2
# Assign a high value to the class number 7
z[7] = 3
# Compute softmax probabilities for each input value
softmax_probs = softmax(z)
# Plot the bar plot
plt.rcParams['axes.axisbelow'] = True
plt.barh(range(num_classes), softmax_probs, color='blue',alpha=1)
plt.yticks(range(num_classes), range(num_classes))
plt.title('Softmax Function')
plt.xlabel('Probability')
plt.ylabel('Class')
plt.grid(axis='x')
plt.xlim([0,1])
plt.show()Output: